For women with thrombophilia, pregnancy is a matter that creates a lot of uncertainty. Many have just learned that they suffer after repeated miscarriages for no apparent reason, which worries even more about the possibility of getting a pregnancy to term.
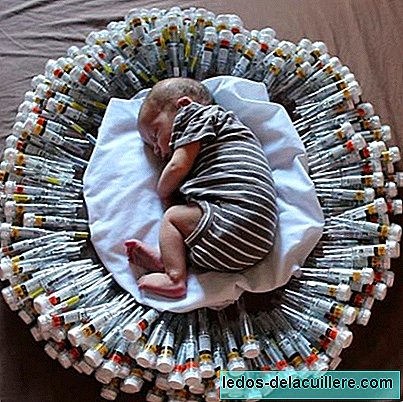
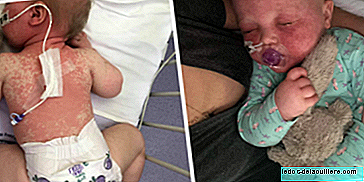
But being a mother with thrombophilia is possible With proper treatment. This shocking picture of a baby about all the doses his mother has injected every day of pregnancy It proves it.
What is thrombophilia?
Thrombophilia is a disorder in the blood coagulation system. It manifests as an alteration in the balance between the formation and destruction of clots, which predisposes to develop thrombotic phenomena, such as formation of arterial or venous clots.
It can be inherited (transmitted from parents to children through gene mutations) or acquired. The most frequent acquired thrombophilia is the "Antiphospholipid syndrome or SAF"It is an autoimmune disease that affects 5 percent of pregnant women that causes the mother's body to create antibodies that attack the placenta.
The formation of clots in pregnancy can clog the blood vessels and hinder the adequate oxygenation and nutrition of the baby, putting your life at risk.
Many times thrombophilia, known as a silent evil. Most people with thrombophilia have no signs or symptoms. The first sign may be that you have a health problem related to a blood clot or when the woman has suffered several repeat abortions. Up to three recurrent pregnancies are not suspected of having a problem.
It should be mentioned that there are about 10 different types of thrombophilia and not all of them are related to complications during pregnancy. That is, not every woman with thrombophilia has pregnancy complications.
Pregnant with thrombophilia

When thrombophilia is confirmed by a blood test, strict medical monitoring during pregnancy is essential. Without treatment, the chances of having a healthy baby are reduced to 20 percent, instead with the right treatment the chances increase to more than 80 percent.
The treatment involves administering an anticoagulant called heparin (low molecular weight or unfractionated) to prevent clot formation and platelet agglomeration that could put the baby at risk.
It is usually administered throughout pregnancy and sometimes extends a few weeks after delivery. There are studies that have proven that the combination of heparin with low doses of aspirin, make the most effective treatment to prevent the loss of the baby.
Prenatal control is completed with Doppler ultrasound to check the blood flow that is reaching the baby and with heart rate monitoring to make sure you are getting enough oxygen.
The risks of thrombophilia in pregnancy
The main risks, which in turn are the main symptoms of thrombophilia, are having three or more spontaneous abortions in the first trimester or lifeless birth during the second or third trimester, intrauterine growth retardation or preeclampsia.
There are also cases of placental abruption, which in turn can cause severe bleeding and its subsequent consequences.
If you have had a blood clotting problem or have a family history of thrombophilias and are planning to find a pregnancy, talk to your doctor about the possibility of testing for the disease. The diagnosis is made through a specific blood test.